The industrial sector is a cornerstone of global economic development, responsible for producing essential goods and services. However, it also accounts for a significant portion of global energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. With growing global commitments to sustainability, industries are under increasing pressure to optimize energy use and reduce their environmental footprint. One of the most promising pathways is waste heat recovery, which captures and utilizes heat that would otherwise be lost in industrial processes. Despite its potential, waste heat recovery faces significant hurdles, especially at low temperatures where corrosion and fouling inhibit the performance of traditional materials.
By Julia Klein, Market Development Manager, Technoform
Technoform, a specialist in thermally and mechanically optimized profile solutions, offers an innovative material, PPS-GR, to overcome these challenges. This advanced thermoplastic polymer with graphite filler redefines the possibilities of heat recovery and CO2 capture in corrosive environments. Combining high thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and ease of integration, PPS-GR is unlocking new opportunities for sustainable industrial processes.
Unlocking the potential of waste heat
Industrial waste heat represents an enormous but underutilized energy resource. According to Heat Roadmap Europe, waste heat from industrial processes could provide energy to power 100 million two-person households. A significant portion of this heat—about one-third—is at temperatures below 200°C. This low-temperature heat, often dismissed as too challenging or inefficient to recover, holds vast potential for reducing energy consumption and emissions if the right technologies are applied. The main challenge lies in recovering heat below the acid and water dew point, where flue gases condense, forming corrosive acids. Traditional materials used in heat exchangers, such as stainless steel or titanium, are often insufficient to withstand these harsh conditions. As a result, industries face frequent equipment failures, high maintenance costs, and suboptimal energy recovery rates. In 2016, NACE International reported that the global cost of general corrosion amounted to USD 2.5 trillion annually. In power plants, where heat exchangers are vital for energy recovery, corrosion-related costs alone exceed USD 7 billion each year. These figures underscore the urgency of finding new materials capable of performing in these demanding conditions.
PPS-GR: a game-changing material
Technoform’s PPS-GR is an innovative composite material designed to address the challenges of low-temperature heat recovery in corrosive environments. Combining polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), a high-temperature-resistant polymer, with graphite, known for its excellent thermal conductivity and acid resistance, PPS-GR delivers unmatched performance in industrial heat exchangers.
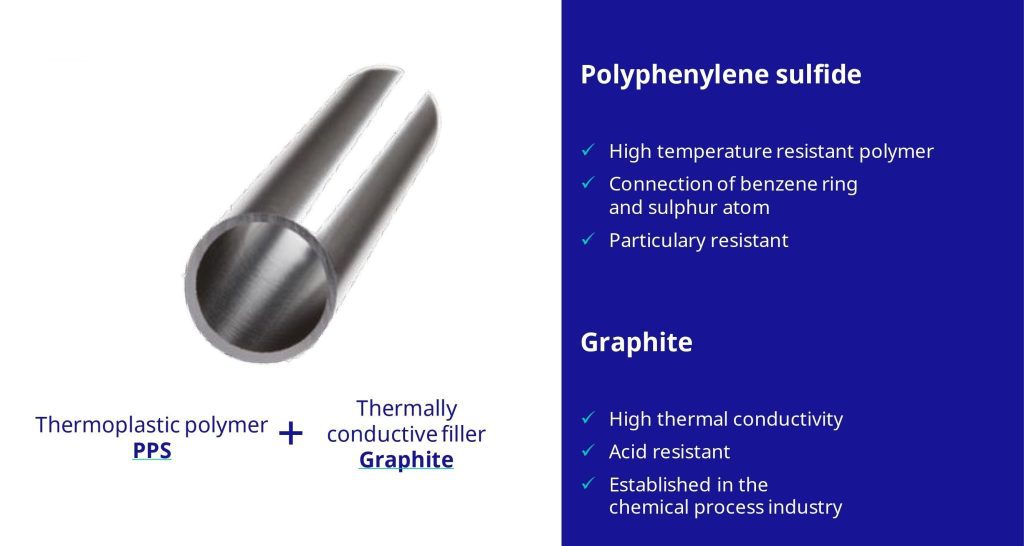
Key properties of PPS-GR:
- Exceptional corrosion resistance: PPS-GR is highly resistant to chemical reactions, even under exposure to corrosive acids and high-pressure environments. This durability ensures longer operational lifespans for heat exchangers and reduces maintenance costs.
- High thermal efficiency: The inclusion of graphite significantly enhances the material’s thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer in low-temperature applications where traditional materials fall short.
- Ease of integration: PPS-GR can be easily incorporated into heat exchangers using simple sealing systems such as single or double O-rings or rubber grommets, which provide a reliable and adaptable sealing solution. These sealing options simplify installation and maintenance, reducing downtime and costs.
- Glass fiber reinforcement: PPS can also be reinforced with glass fibers, improving its structural integrity and making it ideal for use in components subjected to high mechanical stress, such as tube sheets and housings. This reinforcement expands the material’s versatility, allowing it to perform effectively in demanding industrial applications.
A deeper look: Why corrosion matters and its role in sustainability
Corrosion is one of the most persistent challenges faced by industrial operations, particularly in heat exchangers where materials are exposed to extreme temperatures, pressures, and chemically aggressive environments. Over time, corrosion gradually reduces material thickness, undermining the structural integrity and thermal efficiency of equipment. This leads to frequent failures, higher maintenance costs, and reduced overall system performance. For industries operating in corrosive environments, mitigating these effects is critical to maintaining operational reliability and achieving long-term cost savings.
Traditional materials, such as stainless steel or titanium, provide some resistance to corrosion but often require expensive coatings or frequent replacements to maintain performance. PPS-GR eliminates these constraints through its intrinsic resistance to chemical degradation. Its ability to endure harsh conditions without compromising functionality reduces maintenance requirements, minimizes downtime, and extends the lifespan of heat exchangers. This results in a significant reduction in operational costs and environmental impact, as fewer resources are consumed for repairs and replacements. Beyond addressing corrosion, PPS-GR plays a pivotal role in advancing sustainability through heat recovery and decarbonization. Industrial processes generate vast amounts of waste heat, much of it at low temperatures below the acid dew point. Traditionally considered too difficult to recover, this heat represents a largely untapped resource for improving energy efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
PPS-GR’s exceptional thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance make it an ideal material for capturing and repurposing this low-temperature heat. In district heating networks, recovered heat can replace fossil fuels, reducing energy consumption and emissions. In CO2 capture systems, this recovered energy can power the chemical processes required for carbon separation, contributing directly to decarbonization efforts. These applications create a circular energy economy, where waste heat is no longer discarded but instead becomes an asset for sustainable industrial operations. The dual role of PPS-GR in combating corrosion and enabling efficient heat recovery aligns perfectly with global sustainability goals. It supports industries in achieving higher energy efficiency while complying with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. As the push toward net-zero emissions intensifies, innovations like PPS-GR will be instrumental in driving meaningful progress toward a greener, more sustainable future.
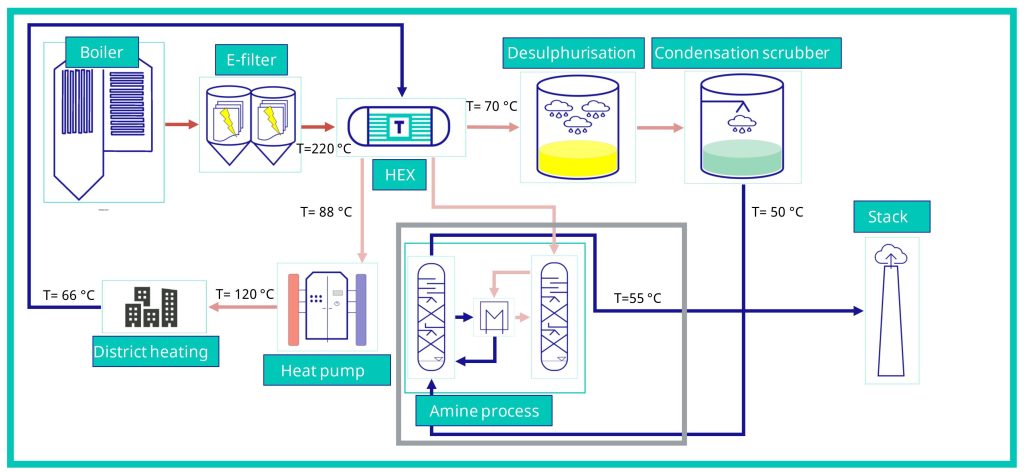
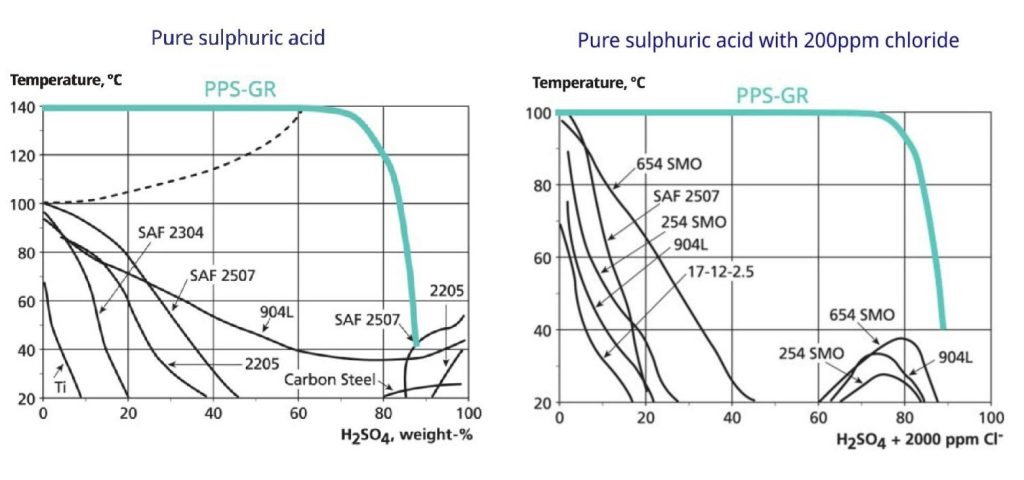
Real-world applications, vision for the future, and conclusion: PPS-GR’s role in transforming industrial sustainability
PPS-GR is more than an innovative material; it is a catalyst for transforming how industries approach energy efficiency and sustainability. Its real-world applications demonstrate its versatility and impact across diverse industrial settings. From recovering heat below the acid dew point in large combustion plants to enabling efficient CO2 capture systems, PPS-GR has consistently delivered measurable benefits. By integrating recovered heat into district heating networks, industries can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, cutting both costs and emissions.
The success of PPS-GR lies in its ability to address pressing industrial challenges while aligning with global sustainability goals. Its high thermal conductivity and exceptional corrosion resistance make it uniquely suited for demanding environments where traditional materials fall short. By reducing maintenance needs, extending equipment lifespans, and enhancing operational efficiency, PPS-GR not only lowers operational costs but also helps industries comply with stringent environmental regulations. Looking ahead, Technoform envisions an even broader role for PPS in shaping the future of energy-intensive industries. Beyond its current applications, the material’s potential extends to structural components such as tube sheets and housings, further expanding its utility in industrial heat exchangers. With features like glass fiber reinforcement for added strength, PPS is equipped to handle diverse and challenging industrial requirements.
Technoform is committed to continuous innovation, ensuring that PPS-GR evolves to meet the dynamic needs of modern industries. By driving progress in low-temperature heat recovery and supporting the transition to a circular energy economy, PPS-GR embodies the principles of sustainability, efficiency, and economic viability. It is a material not only for the present but also for the future, providing industries with the tools they need to thrive in an era of transformation. As the global push for sustainability intensifies, materials like PPS-GR will play a central role in achieving meaningful progress. By enabling industries to recover waste heat, reduce emissions, and optimize energy use, PPS-GR is redefining what’s possible in industrial operations. Its proven performance and versatility make it a cornerstone of sustainable practices, helping industries worldwide build a greener, more energy-efficient future.
About the author

Julia Klein has over ten years of experience working in China. In her current role, she works on expanding the market in the Asia-Pacific region for Technoform’s heat transfer solutions. She focuses on preparing the way for sustainable industrial heat exchangers into China. Julia’s knowledge of international trade and her experience with the Chinese market help her bring new ideas to the industry.
About this Technical Story
This Technical Story was first published in Heat Exchanger World Magazine in February 2025. To read more Technical Stories and many other articles, subscribe to our print magazine.
Technical Stories are regularly shared with our Heat Exchanger World community. Join us and share your own Technical Story on Heat Exchanger World online and in print.

